Indexed Universal Life (IUL) investments have quietly gained traction as a remarkably successful wealth-building strategy in recent years, as traditional investment vehicles have experienced increasingly unpredictable swings. A flexible, tax-advantaged method of safeguarding and increasing personal wealth, an IUL combines the stability of insurance with the energy of the stock market.
For investors looking for balance, IUL policies offer a very clear value proposition by combining market-linked interest with built-in protection against downturns. Similar to a well-designed safety harness that enables a climber to reach daring altitudes without worrying about falling, the design of IULs remarkably lowers risk while maintaining the possibility of moderate growth.
| Information | Details |
|---|
| Product Name | Indexed Universal Life Insurance (IUL) |
| Index Options | S&P 500, Nasdaq-100, among others |
| Growth Mechanism | Capped gains, guaranteed minimum floors |
| Flexibility Offered | Adjustable premiums and death benefits |
| Authentic Reference | Investopedia – Indexed Universal Life Overview |
The Exceptionally Successful Architecture of IUL Investment
In contrast to conventional stock market investing, where profits and losses fluctuate greatly, IULs offer a particularly useful feature called the “floor.” Your cash value is normally protected from losses, usually with a guaranteed minimum return of 0%, even if the stock index associated with your policy crashes.
Policyholders can take part in market growth without fully exposing themselves to the chilling volatility that frequently shakes portfolios thanks to this built-in safety net. IUL providers can offer upside participation, albeit within limits, while still providing this crucial layer of protection by strategically partnering with major indexes such as the S&P 500.
Knowing the Structure: Participation Rates, Floors, and Caps
Three financial tools—caps, floors, and participation rates—that are expertly designed to strike a balance between risk and reward are at the core of an IUL’s structure.
Floor Rate: The minimum guaranteed return on your account that protects you from catastrophic losses even in the event of a market downturn.
The cap rate, which keeps expectations from getting out of control during market booms, is the highest interest rate you can earn.
Participation Rate: A predetermined proportion of market gains that are credited to your account; usually, this ranges from 80% to 100%.
Insurers can protect investors from full exposure during negative cycles while letting them enjoy a share of the market’s positive performance by carefully integrating these controls. This structure is especially novel for investors who value consistent, long-term growth.
Is Investing in IUL Always the Best Option?
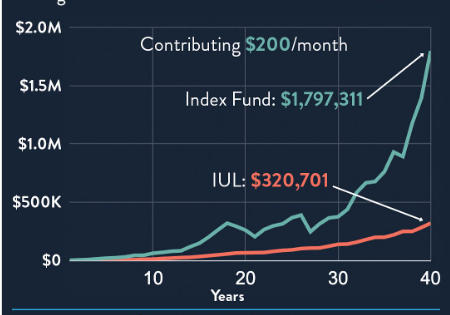
IULs have drawbacks despite being incredibly alluring to a lot of investors. In contrast to direct stock investments, participation rates may result in lower returns, and caps may limit possible gains during booming markets. Furthermore, if the policyholder takes money out too soon, fees and surrender charges can drastically lower the cash value.
Direct exposure via index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) can produce noticeably faster returns without caps in the context of pure investing. However, IULs provide a very flexible and reliable option for people who value protection, flexibility, and tax benefits all at once.
Why IUL Is Considered a Growing Force by Financial Experts
IUL investments are becoming more and more recognized by financial advisors as an essential component of a diversified portfolio, especially for high-net-worth individuals and business owners looking to strike a balance between liquidity, growth, and legacy planning.
Numerous people’s retirement planning strategies have been significantly enhanced by IUL policies, which take advantage of tax-deferred growth, flexible premium payments, and lifetime death benefits. Additionally, cash allocations between fixed and index-linked accounts can be tailored to reflect changing market conditions through strategic alliances between policyholders and insurers.